-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
Commit
This commit does not belong to any branch on this repository, and may belong to a fork outside of the repository.
- Loading branch information
Showing
8 changed files
with
416 additions
and
503 deletions.
There are no files selected for viewing
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,40 @@ | ||
| # Big O Notation | ||
|
|
||
| [Big O complexity chart & explanation](https://towardsdatascience.com/understanding-time-complexity-with-python-examples-2bda6e8158a7) | ||
|
|
||
| 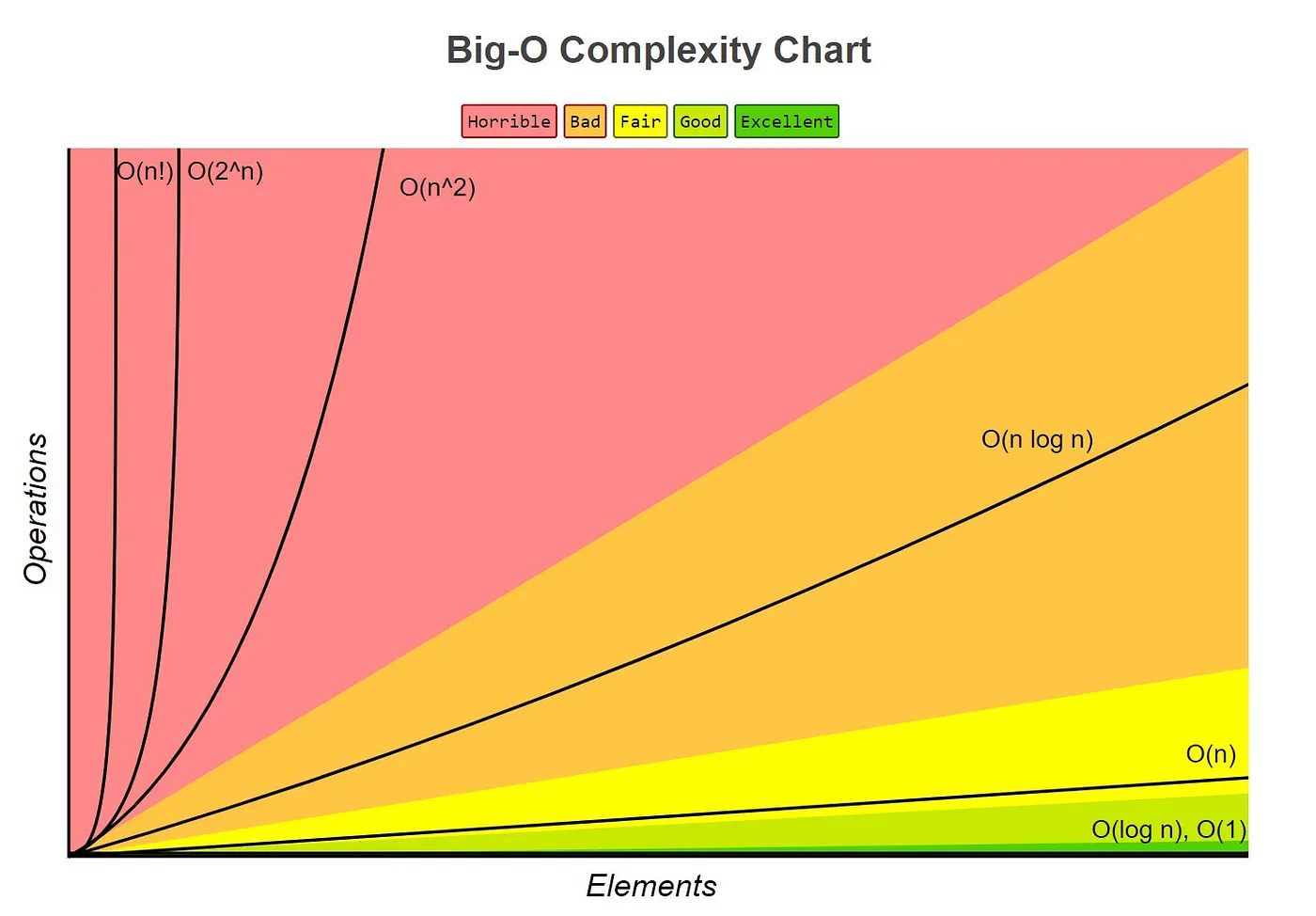 | ||
|
|
||
| ## Time complexity | ||
|
|
||
| - Excellent 🟩 | ||
| - `O(1)` - constant (no loops, assignment) | ||
| - `O(log n)` - logarithmic (usually searching algorithms have log n if they are sorted (Binary Tree Search)) Divide & Conquer | ||
| - Fair 🟨 | ||
| - `O(n)` - linear (single loop of n items) | ||
| - Bad 🟧 | ||
| - `O(n log n)` - log linear (usually sorting operations) | ||
| - Horrible 🟥 | ||
| - `O(n^2)` 🐌 - quadratic (2 nested loops, comparing with each element in array) | ||
| - `O(2^n)` 🐌🐌 - exponential (recursive algorithms that solves a problem of size N) | ||
| - `O(n!)` 🐌🐌🐌 - factorial (nested loop for every element) | ||
|
|
||
| ## Rules - how to calculate f() complexity | ||
|
|
||
| - Rule 1: Worst Case | ||
| - Rule 2: Remove Constants | ||
| - Rule 3: Different terms for inputs (a+b) (a*b) (next operation: +, nested operation:*) | ||
| - Rule 4: Drop Non Dominants | ||
|
|
||
| ## What causes TIME complexity | ||
|
|
||
| - operations (+, -, *, /) | ||
| - comparisons (<, >, ==) | ||
| - looping (for, while) | ||
| - outside function call (function()) | ||
|
|
||
| ## What causes SPACE complexity | ||
|
|
||
| - variables | ||
| - data structures | ||
| - function call | ||
| - allocations |
This file was deleted.
Oops, something went wrong.
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,24 @@ | ||
| # Depth First Search (DFS) | ||
|
|
||
| [Depth First Search (DFS)](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Depth-first_search) - an algorithm for traversing or searching tree or graph data structures. The algorithm starts at the root node and explores as far as possible along each branch before backtracking. | ||
|
|
||
| Create a function that, given a DOM Element on the page, will visit the element itself and all of its descendent (not just its immediate children). For each element visited, the function should pass that element to a provided callback function. | ||
|
|
||
| The arguments to the function should be: | ||
|
|
||
| - a DOM element | ||
| - a callback function (that takes a DOM element as its argument) | ||
|
|
||
| ```js | ||
| // Visiting all elements in a tree (DOM) is a classic Depth-First-Search algorithm application | ||
|
|
||
| function Traverse(p_element, p_callback) { | ||
| p_callback(p_element); | ||
|
|
||
| var list = p_element.children; | ||
|
|
||
| for (var i = 0; i < list.length; i++) { | ||
| Traverse(list[i], p_callback); // recursive call | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| ``` |
This file was deleted.
Oops, something went wrong.
Oops, something went wrong.