This README describes how to deploy elasticsearch + kibana either locally or on gcloud using Kubernetes.
The following dependencies must be installed on your laptop:
-
python2.7
-
a copy of this github repo
git clone https://github.com/macarthur-lab/elasticsearch-kubernetes-cluster.git -
install this repo's python dependencies
cd elasticsearch-kubernetes-cluster; pip install -r requirements.txt
Local Dev. Instance on MacOSX
The local installation relies on Kube-Solo (https://github.com/TheNewNormal/kube-solo-osx/releases) which is a low-overhead VM for running Kubernetes on a MacOSX laptop.
-
Install CoreOS, which is required for for Kub-Solo:
a.
brew install libev
b. Install the latest DMG from https://github.com/TheNewNormal/corectl.app/releasesWARNING:Being on a VPN connection may cause errors during CoreOS install steps that need to download components from the web. The solution is to disconnect from VPN. -
Install Kube-Solo: https://github.com/TheNewNormal/kube-solo-osx/releases
-
Install kubectl: https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/kubectl/install/
-
Initialize:
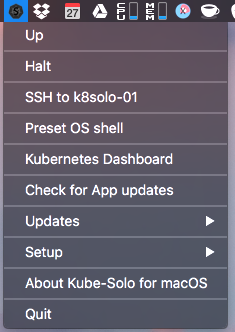
a. When launching Kube-Solo for the 1st time, click on
Setup > Initial Setup of Kube-Solo VMIt will open an iTerm2 shell and ask for several inputs. The following settings are recommended:Set CoreOS Release Channel: 3) Stable (recommended) Please type VM's RAM size in GBs: 8 Please type Data disk size in GBs: 20b. After this initial setup, you can just click
Preset OS Shellto open a new terminal where docker and kubectl are preconfigured to use the local kubernetes cluster. -
Trouble-shooting Kube-Solo VM setup issues: If your computer goes to sleep or reboots, the CoreOS / Kube-Solo VM may become unresponsive, requiring it to be rebooted (or possibly even reinitialized)
For some reason,
The following steps fail if you're connected to a VPNso be sure to disconnect before proceeding.
You can click
Haltand thenUpin the Kube-Solo menu to shut-down and then restart the VM. This typically resolves most issues. If Halt takes a long time, runningpkill kubeon the command-line may help. Previously-deployed components will automatically start up when the VM restarts.If issues persist, you can delete and reinitialize the Kube-Solo VM by Halting it and then running
rm -rf ~/kube-solo. If you then clickUpin the Kube-Solo menu, it will reinitialize the VM from scratch.
Production Instance on Google Cloud
Google Container Engine makes it easy to create a Kubernetes cluster and then deploy, manage, and scale an application. The following steps are necessary before ./servctl can be used to deploy to a Google Container Engine cluster:
-
Install Docker for MacOSX:
https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-mac/install/It will be used to build docker images before pushing them to your private repo on Google Container Engine.
-
Install kubectl: https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/kubectl/install/
*-settings.yaml - contain settings for local, dev and prod deployments.
To deploy all services to your Kubernetes cluster, run:
./servctl deploy {label} # label can be 'local', 'gcloud-dev'
The ./servctl script also provides subcommands for performing common steps for managing and troubleshooting:
deploy # Deploy one or more components
logs # show logs for one or more components
port-forward # start port-forwarding for service(s) running in the given component container(s), allowing connections via localhost
connect-to # start port-forwarding and show logs for the given component
shell # open a bash shell inside one of the component containers
status # print status of all kubernetes and docker subsystems
dashboard # open the kubernetes dasbhoard in a browser
delete # delete pods and resources for a specific component - opposite of deploy
delete-all # delete all resources and components and also (optionally) the VM(s) they were running on
- Official Kuberentes User Guide: https://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/
- 15 Kubernetes Features in 15 Minutes: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=o85VR90RGNQ
- Kubernetes: Up and Running: https://www.safaribooksonline.com/library/view/kubernetes-up-and/9781491935668/
- The Children's Illustrated Guide to Kubernetes: https://deis.com/blog/2016/kubernetes-illustrated-guide/