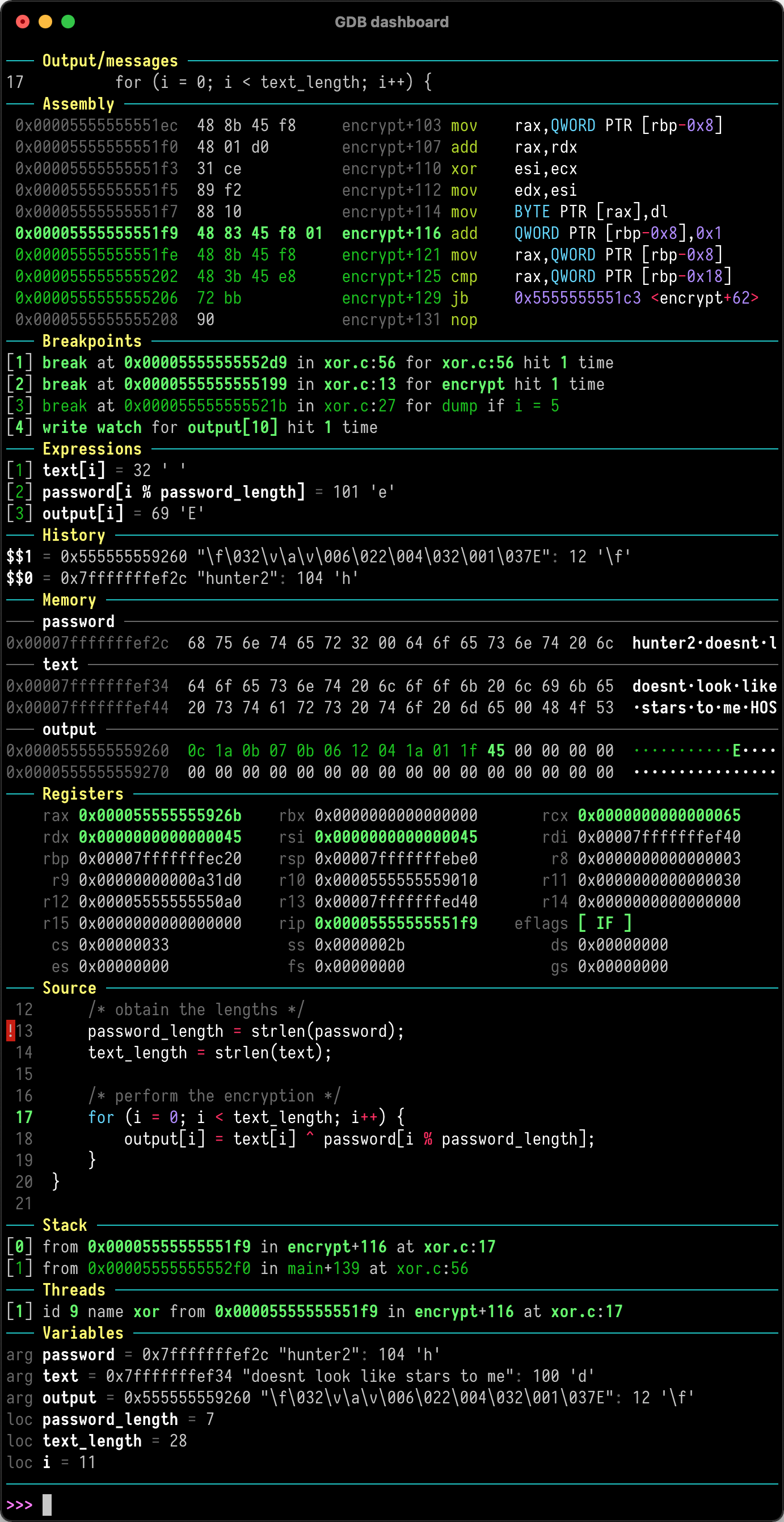
GDB dashboard is a standalone .gdbinit file written using the Python API that enables a modular interface showing relevant information about the program being debugged. Its main goal is to reduce the number of GDB commands needed to inspect the status of current program thus allowing the developer to primarily focus on the control flow.
Just place .gdbinit in your home directory, for example with:
wget -P ~ https://git.io/.gdbinit
Optionally install Pygments to enable syntax highlighting:
pip install pygments
Then debug as usual, the dashboard will appear automatically every time the inferior program stops.
Keep in mind that no GDB command has been redefined, instead all the features are available via the main dashboard command (see help dashboard).
Program a function such as std::string debug(BinaryTree& tree) which returns a string which shows tree directly like this:
╭╴d
╭╴a
c
│ ╭╴e
╰╴b
╰╴fThen edit you gdb script like this.
python
user_methons['BinaryTree'] = 'debug'
endLet's name you script "gdb.binary-tree", then run gdb -x gdb.binary-tree, then dashboard will call BinaryTree(debug).
Then you tree will look like this.
You'd better NEVER USE A VALUE NAME repeatly, or you may not get right resualt.
Head to the wiki to learn how to perform the most important tasks.