|
| 1 | +# CS231n 6강(혜주) |
| 2 | + |
| 3 | +다음은 스탠포드 대학 강의 [CS231n: Convolutional Neural Networks for Visual Recognition](http://cs231n.stanford.edu/) 을 요약한 것입니다. |
| 4 | + |
| 5 | + |
| 6 | + |
| 7 | +6강의 내용을 도식화해서 정리하면 다음과 같습니다. |
| 8 | + |
| 9 | + |
| 10 | + |
| 11 | + |
| 12 | + |
| 13 | + |
| 14 | + |
| 15 | +## 1. Activation Functions |
| 16 | + |
| 17 | +### 1) Sigmoid function |
| 18 | + |
| 19 | +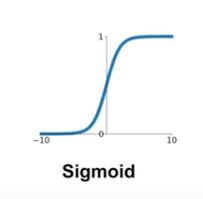 |
| 20 | + |
| 21 | +- 특징 |
| 22 | + - output의 범위가 0과 1이 되게 한다. |
| 23 | + - neuron의 firing rate을 잘 나타낸다고 생각되어서 인기가 많았다. |
| 24 | +- 단점 |
| 25 | + - 극단값들의 gradient는 결국 0이 되어 의미가 없어진다. |
| 26 | + - sigmoid의 output은 0이 중심이 되지 않는다. -> 항상 양수인 input이 들어오면 w에 대한 gradient는 모두 양수이거나 음수가 된다 -> w vector가 비효율적으로 찾아진다. |
| 27 | + - 함수에 exp()이 들어가서 computing이 비효율적이다. |
| 28 | + |
| 29 | + |
| 30 | + |
| 31 | +### 2) ReLU function |
| 32 | + |
| 33 | +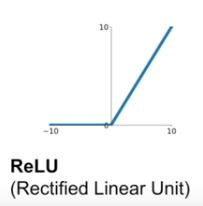 |
| 34 | + |
| 35 | +**f(x) = max(0,x)** |
| 36 | + |
| 37 | + |
| 38 | + |
| 39 | +- 특징 |
| 40 | + - (+)부분에서 output 부분을 뭉개지 않는다. |
| 41 | + - exp()이 없어서 컴퓨팅적으로 효율적이다. |
| 42 | + - sigmoid나 tanh보다 빨리 converge한다. |
| 43 | + - sigmoid보다 neuron의 작용을 더 잘 반영한다. |
| 44 | +- 단점 |
| 45 | + - 역시 0이 중심인 output은 아니다. |
| 46 | + - 0보다 작은 부분의 gradient는 0이 되어버린다. |
| 47 | + |
| 48 | + |
| 49 | + |
| 50 | +ReLU를 보완한 Leaky ReLU, PReLU등이 있다. |
| 51 | + |
| 52 | +실제적으로 ReLU를 사용하면 좋다. (단, learning rate설정 유의) |
| 53 | + |
| 54 | +sigmoid는 별로 효과가 좋지 않다. 초반에 나온 것이라 사용되었던 거지 지금은 ReLU를 많이 쓴다고 한다. |
| 55 | + |
| 56 | + |
| 57 | + |
| 58 | + |
| 59 | + |
| 60 | +## 2. Data Preprocessing |
| 61 | + |
| 62 | +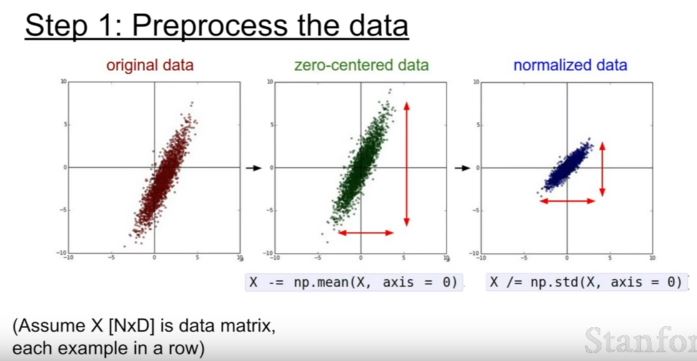 |
| 63 | + |
| 64 | +데이터 전처리에 주로 zero-centering을 많이 사용한다. 이미지 처리에서는 normalization까지 하지는 않는다. |
| 65 | + |
| 66 | + |
| 67 | + |
| 68 | +## 3. Weight Initialization |
| 69 | + |
| 70 | +weight을 처음에 어떻게 시작하는지에 따라 학습 과정이 달라질 수 있으므로 weight initialization은 중요하다. |
| 71 | + |
| 72 | +1) 작은 랜덤 숫자로 시작? **sd=0.01** |
| 73 | + |
| 74 | +**W = 0.01* np.random.randn(D,H)** |
| 75 | + |
| 76 | +작은 네트워크에서는 괜찮지만, 네트워크의 깊이가 깊어지면 분산이 0으로 가기 때문에, 아래와 같이 데이터들이 줄어든다. 즉, 모든 activiation이 0 이 되어버린다. 이에 따라 upstreaming gradient가 0이 된다. |
| 77 | + |
| 78 | + |
| 79 | +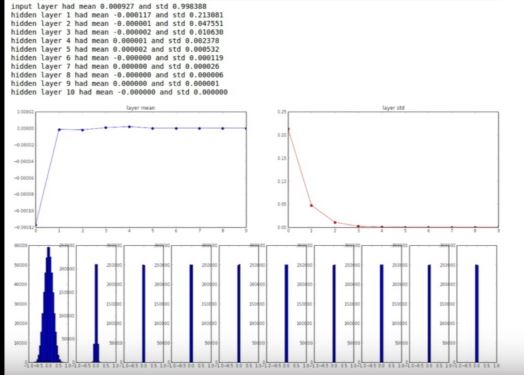 |
| 80 | + |
| 81 | + |
| 82 | + |
| 83 | +2) **sd=1로 설정하면?** |
| 84 | + |
| 85 | +하단과 같이 모든 뉴런이 -1아니면 1이 되어버려 gradient는 모두 0 이 되어버린다. |
| 86 | + |
| 87 | + |
| 88 | + |
| 89 | + |
| 90 | +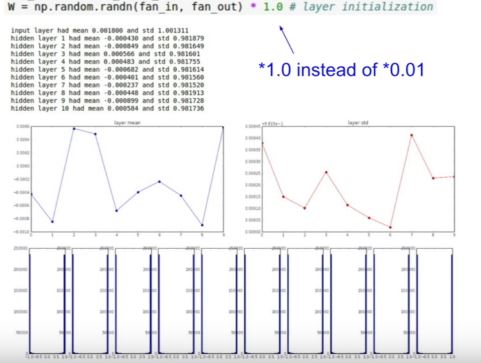 |
| 91 | + |
| 92 | + |
| 93 | +3) Xavier Initialization |
| 94 | + |
| 95 | +``` W = np.random.randn(fan_in,fan_out) / np.sqrt(fan_in)``` |
| 96 | + |
| 97 | +적절한 initialization을 만들어주는 방법이다. |
| 98 | + |
| 99 | +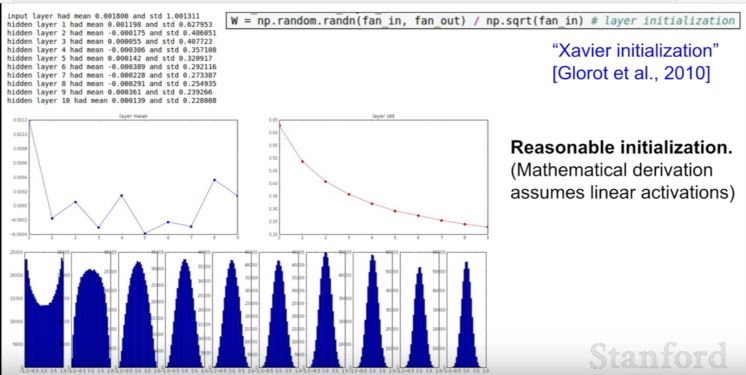 |
| 100 | + |
| 101 | +그러나 ReLU에 사용하면 제대로 작동하지 않는다. 하단과 같이 보충한다. |
| 102 | + |
| 103 | + ` W = np.random.randn(fan_in,fan_out) / np.sqrt(fan_in/2)` |
| 104 | + |
| 105 | + |
| 106 | + |
| 107 | +## 4. Batch Normalization |
| 108 | + |
| 109 | +batch normalization은 batch의 dimension마다 unit gaussain activation을 만들어주는 과정이다. |
| 110 | + |
| 111 | + |
| 112 | + |
| 113 | + |
| 114 | +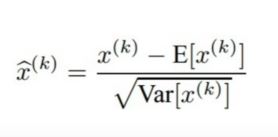 |
| 115 | + |
| 116 | + |
| 117 | + |
| 118 | +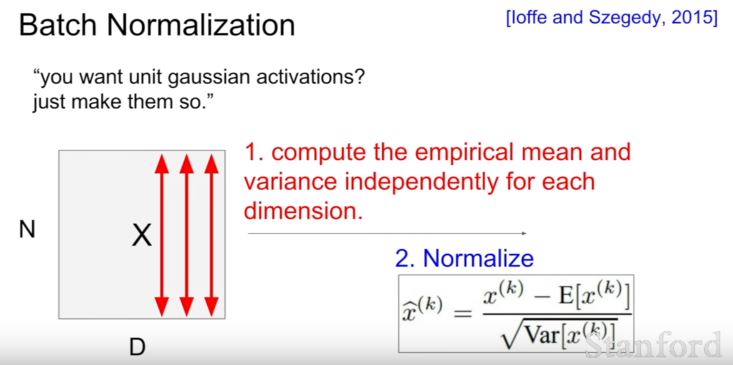 |
| 119 | + |
| 120 | +1. dimension에 따라 평균과 분산 계산 |
| 121 | +2. 식에 따라 normalize |
| 122 | + |
| 123 | + |
| 124 | + |
| 125 | +- 위치: FC layer 혹은 Convolutional layer 뒤, 그리고 nonlinearity function 앞. |
| 126 | +- normalize 한 것을 다시 되돌리기 위해 하단의 식을 사용한다. |
| 127 | + |
| 128 | +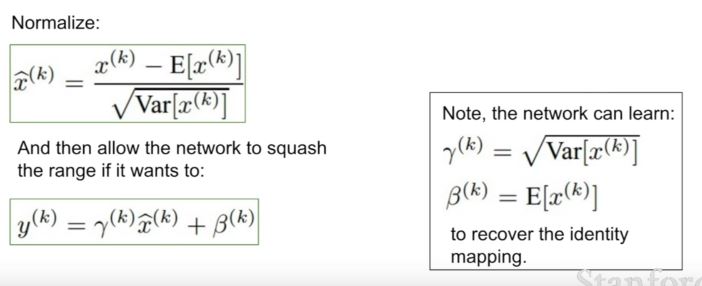 |
| 129 | +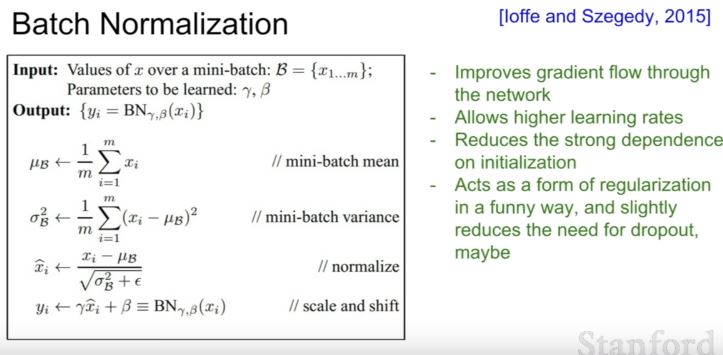 |
| 130 | + |
| 131 | +- 특징 |
| 132 | + - gradient flow 향상 |
| 133 | + - 좀 더 높은 learning rate 가능하게 함 |
| 134 | + - initialization에 대한 의존도를 줄인다 |
| 135 | + |
| 136 | + |
| 137 | + |
| 138 | +## 5. Babysitting Learning Process |
| 139 | + |
| 140 | +학습 과정을 간단히 정리하면, |
| 141 | + |
| 142 | +첫번째 step: 데이터 전처리 |
| 143 | + |
| 144 | +두번쨰 step: 구조를 선택한다. |
| 145 | + |
| 146 | + |
| 147 | + |
| 148 | +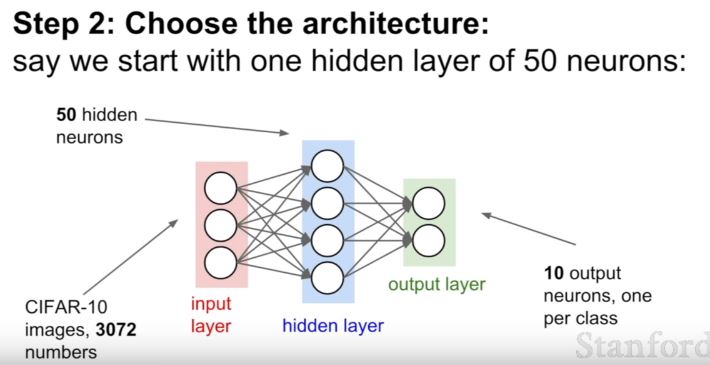 |
| 149 | + |
| 150 | +- loss가 적절한지 확인하는 법 |
| 151 | + - regularization term을 없앴다가 만든다. regularization term을 넣어서 loss가 올라가면 잘 된 거다. |
| 152 | + - loss가 줄어들지 않고 그대로? : learning rate너무 낮아 |
| 153 | + - loss가 폭발적?: learning rate너무 높아 |
| 154 | + - cross validating할 때 대충 [1e-3,..1e-5]면 적당하다고 한다. |
| 155 | + |
| 156 | + |
| 157 | + |
| 158 | +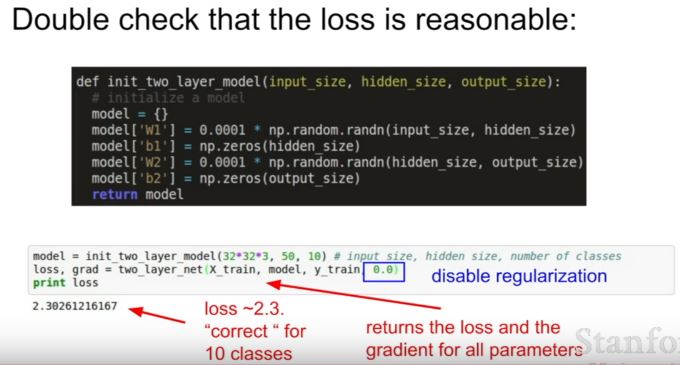 |
| 159 | +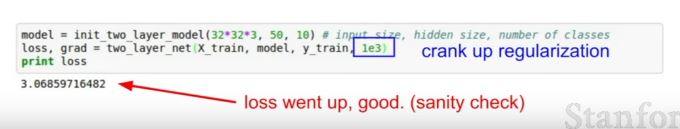 |
| 160 | + |
| 161 | + |
| 162 | + |
| 163 | +- Cross-validation 전략(coarse -> fine) |
| 164 | + - 먼저 coarse하게 대충 어떻게 parameter들이 작동하는지 파악 |
| 165 | + - 이후 fine 하게 parameter찾기 |
| 166 | + |
| 167 | + |
| 168 | + |
| 169 | + |
| 170 | +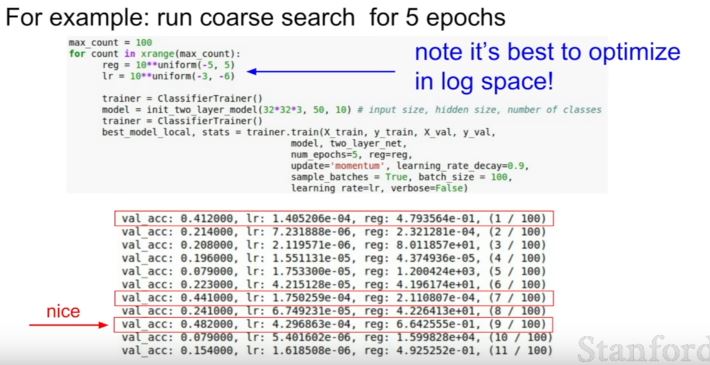 |
| 171 | + |
| 172 | + |
| 173 | + |
| 174 | +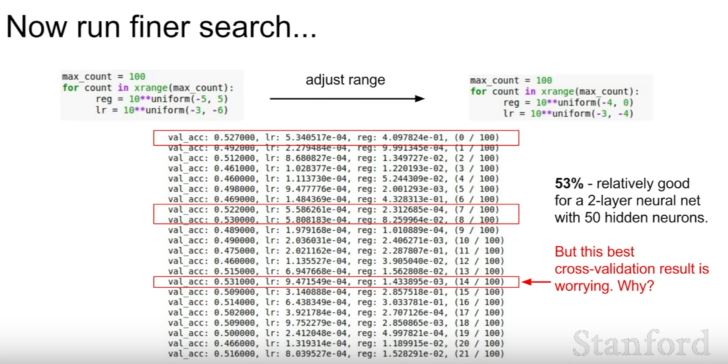 |
| 175 | + |
| 176 | + |
| 177 | + |
| 178 | +- Random Search가 Grid Search보다 좋다. |
| 179 | + |
| 180 | +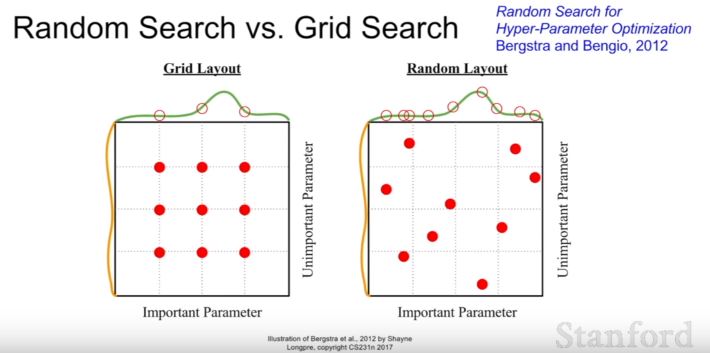 |
| 181 | + |
| 182 | + |
| 183 | + |
| 184 | +- learning rate말고도 network 구조, decay schedule, update type, regularization등 조정해야 할게 많다. 이에 따라 loss function의 작동이 달라지므로. |
| 185 | + |
| 186 | + |
| 187 | + |
| 188 | + |
| 189 | + |
| 190 | +##6. Hyperparmeter Optimization |
| 191 | + |
| 192 | +1) loss curve보기 |
| 193 | + |
| 194 | +good learning rate의 모양 잘 봐두자! |
| 195 | + |
| 196 | +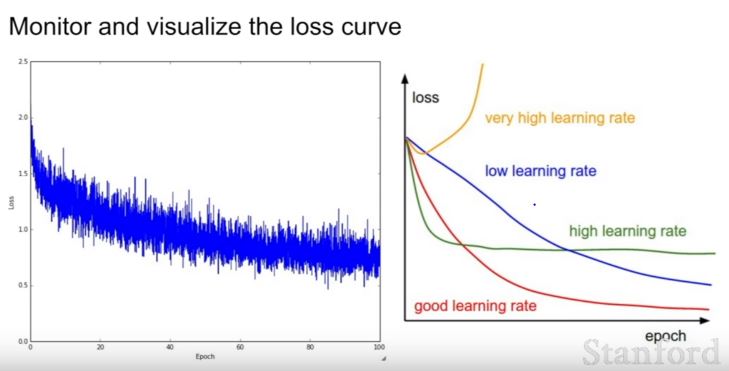 |
| 197 | + |
| 198 | +다음과 같은 형태의 loss curve하면 bad initialization을 의심해봐야 한다. |
| 199 | + |
| 200 | +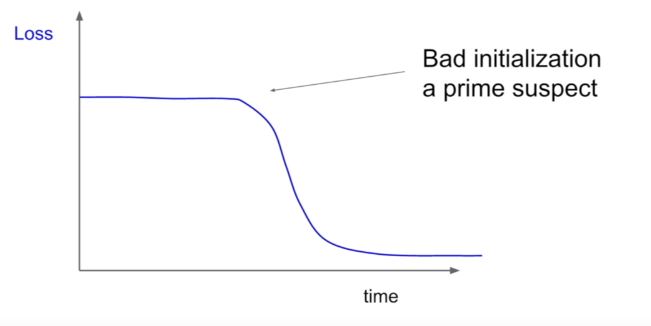 |
| 201 | + |
| 202 | +- train set accuracy vs. validation set accuracy |
| 203 | + - 큰 차이: overfitting문제 |
| 204 | + - 차이 x : overfitting x |
| 205 | + |
| 206 | +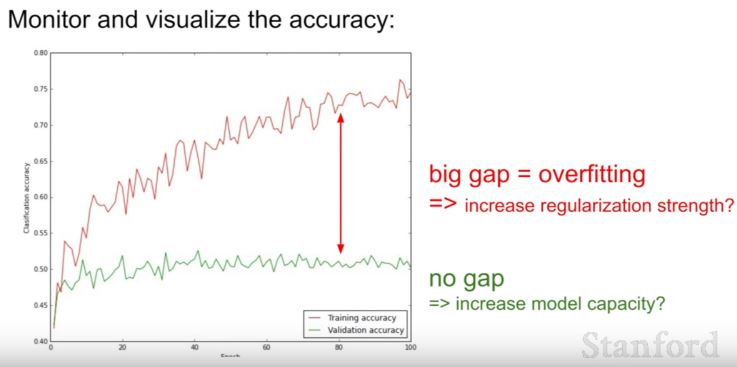 |
| 207 | + |
| 208 | +- weight의 update비율을 확인하고 조정하는 것도 좋은 방법! |
| 209 | + |
| 210 | +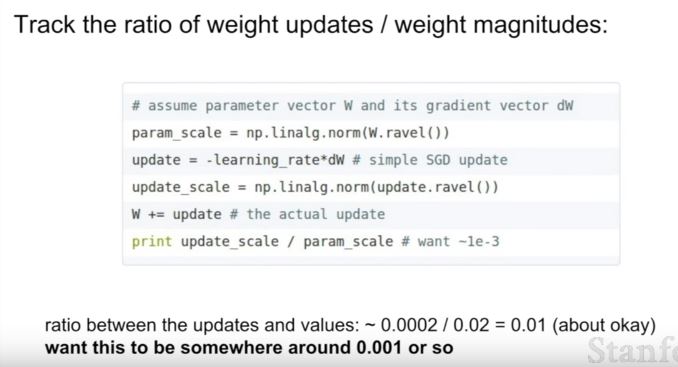 |
| 211 | + |
| 212 | + |
| 213 | + |
| 214 | +## + 강의자님의 요약.. |
| 215 | + |
| 216 | +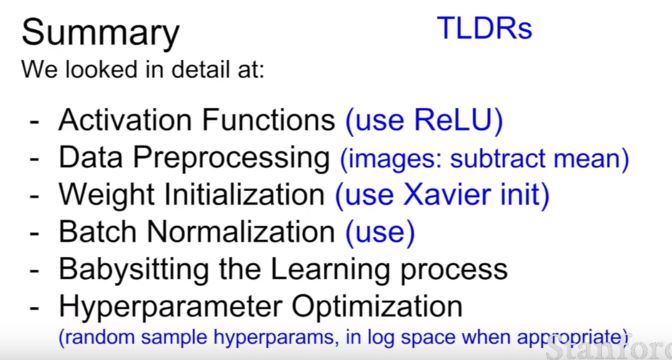 |
| 217 | + |
0 commit comments