-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 1
Domain Analysis
- Web application development is the creation of application programs that reside on remote servers and are delivered to the user’s device over the Internet. A web application does not need to be downloaded and is instead accessed through a network. An end user can access a web application through a web browser such as Google Chrome. A majority of web applications can be written in JavaScript, Cascading Style Sheets (CSS), and HTML5.
- Web application development will typically have a short development life-cycle led by a small development team. Frontend development for web applications is accomplished through client-side programming. Cleint refers to a computer application such as a web browser. Client-side programming will typically utilize HTML, CSS and JavaScript. HTML programming will instruct a browser how to display the on-screen content of web pages, while CSS keeps displayed information in the correct format. JavaScript will run JavaScript code on a web page, making some of the content interactive.
- Server-side programming powers the client-side programming and is used to create the scripts that web applications use. Scripts can be written in multiple scripting languages such as Ruby, Java and Python. Server-side scripting will create a custom interface for the end-user and will hide the source code that makes up the interface.
- A database such as MySQL or MongoDB can be used to store data in web application development.
- Here is a brief look at what is a web application.
- And this is a tutorial for detailed steps for developing a web application.
-
The definition of mobile application development is given as
the process of making software for smartphones, tablets and digital assistants, most commonly for the Android and iOS operating systemsby IBM. -
If you look to ship the application to multiple mobile platforms (most probably Android and iOS), you might go for an all-native approach and create different codebases for different platforms and use OS-specific APIs and programming languages to build a powerful, performant application (using Swift for iOS app development would be a good example). Or you might want to adopt a write-once-use-anywhere approach to speed up the development process. Apps developed using this approach are called
hybrid appsand they are usually built using platform independent languages such as JavaScript, HTML, and CSS. -
Mobile app developers usually take advantage of powerful frameworks to increase their workflow. React Native, for example, is a popular UI framework.
-
The developers should also take into account that mobile devices come in every size and have varying technical specs and ensure that the app is fully-functional (both interactivity and performance-wise) in every possible mobile device.
-
The developers must also take into account that mobile devices, although having improved drastically within the years, are still being run on battery with scarce resources. Therefore, mobile applications must be as light as possible, putting as less pressure on the hardware as possible.
Aim: Data needs to be accessible and available in a standardised format.
Linked Data: A set of design principles for publishing structured machine-readable data that allow to link it with other data.
There are several features of linked data that allow it to interlink with other data. The inventor of the World Wide Web, Tim Berners-Lee, outlined four principles to define them.
URI: Uniform Resource Identifier is a sequence of characters which can give a unique name to virtually anything – digital online content, a real object or an abstract concept.
- URIs allow us to distinguish things and recognize things which are the same.
- URIs must be persistent, permanently assigned to a particular resource.
HTTP: A set of rules for transferring data over the internet. It is the basis of communication between web servers and web browsers.
- We need a standard format to represent the data and to use standard query language to find its metadata (information about the data).
RDF: Resource description framework is a data model currently considered as a standard way to describe data. It defines relationships between data objects using ‘triples’, based on the subject–predicate–object structure which we know from our human language.
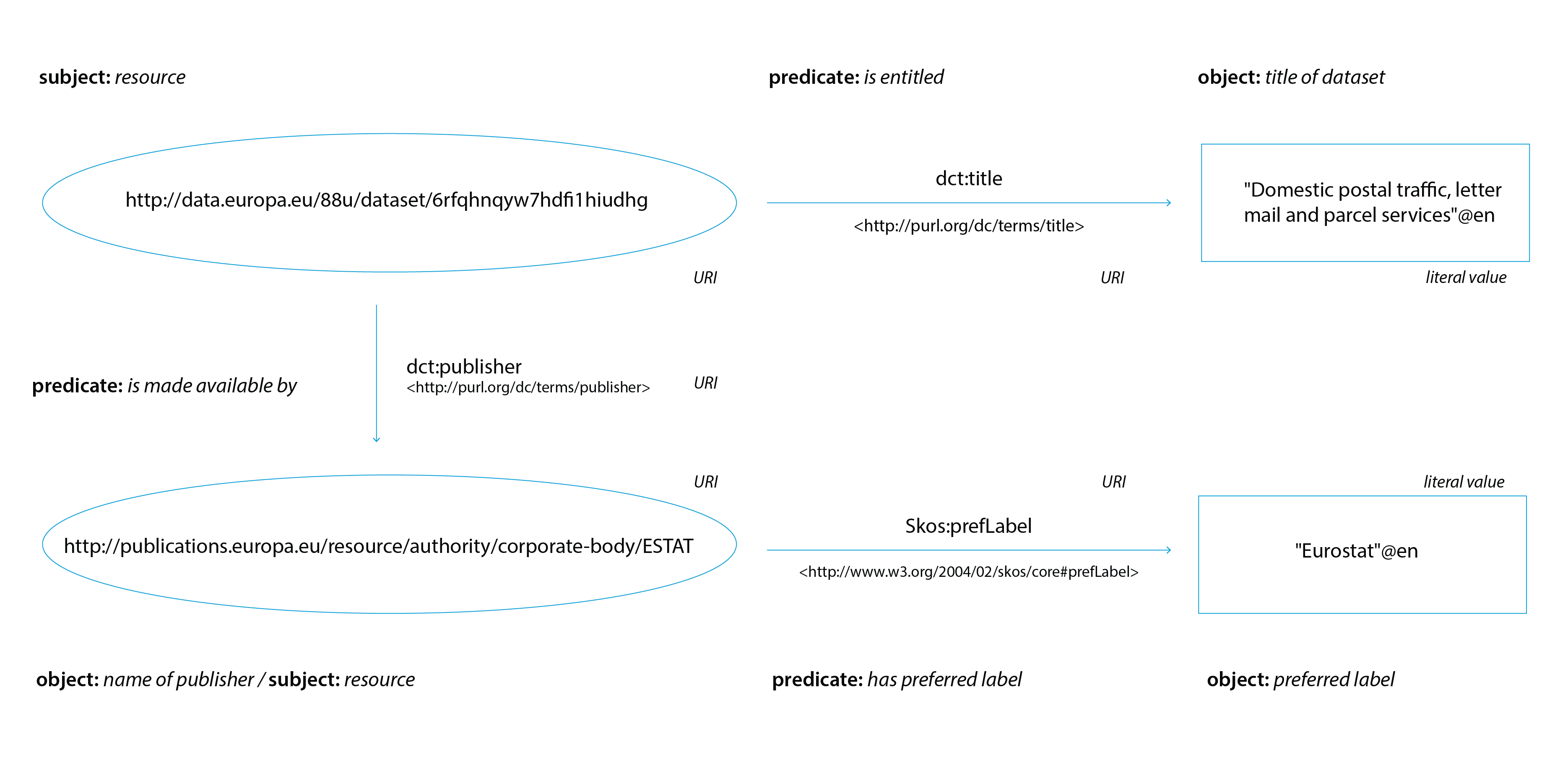
SPARQL: A standardised query language to retrieve and manipulate data stored in RDF format.
- With SPARQL, you can search in multiple data sources in one go using SPARQL endpoints.
- The results of SPARQL queries can be returned in multiple formats, including RDF.
- Adding more links between pieces of data allows us to discover relationships, gives data more context and meaning and ultimately allows us to find more information.
Source: European Data
- A great collection of resources on Linked Data from W3C Wiki.
- MDN Web Docs on HTTP.
- Apache Jena's SPARQL Tutorial.
Wikidata is a free, collaborative, multilingual, secondary knowledge base, collecting structured data to provide support for Wikipedia, Wikimedia Commons, the other wikis of the Wikimedia movement, and to anyone in the world.
Being much stronger than its simple definition, Wikidata API gives access to all the data in Wikipedia and Wikimedia by simple queries.
Modify the url parameter "search" as you wish.
Paste the response to this Online JSON Parser
Even though it can be tuned, below are the most useful url parameters.
- search : The text to search for
- type : Type of entity to search for - item (default), property etc.
- limit : Number of entities to fetch
- continue : Offset to search from (useful for paginating the response)
You can give it a try by just copying and modifying what you would like to search and examine the response.
It also has an API called Sparql.
In very simple terms, one writes a query which is similar to an SQL query, specify some constraints and receives the results accordingly. Using Wikidata Query Service, it is also possible to visualize the result in a location-based manner on the map.
Resources to delve deeper into Sparql:
Note that you can find code versions of your Sparql queries in several programming languages like Python, Java, Javascript and so forth by clicking </>Code button in Wikidata Query Service after making a successful query.
🏠 Home
- Oktay Özel
- Aras Taşçı
- Yunus Emre Özdemir
- Kaan Yolcu
- Elif Nur Deniz
Eymen Çeliktürk- Anıl Köse
Battal Hazar- Halil Özkan
Ebru Özçakı- Ali Tarık Şahin
- Ahmet Oğuz Engin
- Yağız Güldal
- Lab Report 1
- Lab Report 2
- Lab Report 3
- Lab Report 4
- Lab Report 5
- Lab Report 6
- Lab 7 PR
- Lab 8 PR
- Lab Report 9
- Lab Meeting 1
- Weekly Meeting 1
- Lab Meeting 2
- Weekly Meeting 2
- Frontend Meeting 1
- Lab Meeting 3
- Weekly Meeting 3
- Lab Meeting 4
- Frontend Meeting 2
- Weekly Meeting 4
- Weekly Meeting 5
- Frontend Meeting 3
- Lab Meeting 5
- Weekly Meeting 6
- Weekly Meeting 7
- Lab Meeting 6
- Weekly Meeting 8
- Lab Meeting 7
- Lab Meeting 8
- Weekly Meeting 9
- Requirements
- Elicitation Questions
- Project Plan
- Use Case Diagram
- Sequence Diagrams
- Class Diagrams
- Front-End Mockups
- Mobile Mockups
- User Scenario 1
- User Scenario 2
- User Scenario 3
- User Scenario 4
- User Scenario 5
- RAM
- Tags Documentation
- Domain Specific Improvement Ideas
- Lab-6 User Stories
- Customer Milestone 2 Plan
- Software Quality Plan
- Implemented Requirements For Milestone 2
- Customer Milestone 3 Plan
📅 Meetings
- Meeting 1
- Meeting 2
- Meeting 3
- Meeting 4
- Meeting 5
- Meeting 6
- Meeting 7
- Meeting 8
- Meeting 9
- Meeting 10 - Class Diagrams
- Meeting - Frontend 1
- Meeting - Backend 1
- Meeting 11
- Meeting - Backend 2 Wikidata
- Meeting - Frontend 2
- Meeting - Deployment
- Meeting - Frontend 3
- Meeting 12
- Meeting - Backend 3
- Meeting - Backend 4
- Meeting - Frontend 4
- Meeting 13
- Meeting 14
- Meeting 15
- Meeting 16
💻 Project
- Class Diagrams
- Sequence Diagrams
- Use Case Diagrams
- Requirements
- Elicitation Questions
- Project Plan
- Work Done By Each Member
- Milestone Report 1
- Scenarios-Mockups
- Responsibility Assignment Matrix
- Responsibility Assignment Matrix Old Version
- Related Software Analysis
- Workdone Each Member Milestone 2
- Milestone 2 Report
- Work Done By Each Member Milestone 3
- RAM 3
- Milestone Report 3