You signed in with another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.You signed out in another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.You switched accounts on another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.Dismiss alert
[Support] Vendor rpmalloc in-tree and use it for the Windows 64-bit release (#91862)
### Context
We have a longstanding performance issue on Windows, where to this day,
the default heap allocator is still lockfull. With the number of cores
increasing, building and using LLVM with the default Windows heap
allocator is sub-optimal. Notably, the ThinLTO link times with LLD are
extremely long, and increase proportionally with the number of cores in
the machine.
In
llvm/llvm-project@a6a37a2,
I introduced the ability build LLVM with several popular lock-free
allocators. Downstream users however have to build their own toolchain
with this option, and building an optimal toolchain is a bit tedious and
long. Additionally, LLVM is now integrated into Visual Studio, which
AFAIK re-distributes the vanilla LLVM binaries/installer. The point
being that many users are impacted and might not be aware of this
problem, or are unable to build a more optimal version of the toolchain.
The symptom before this PR is that most of the CPU time goes to the
kernel (darker blue) when linking with ThinLTO:
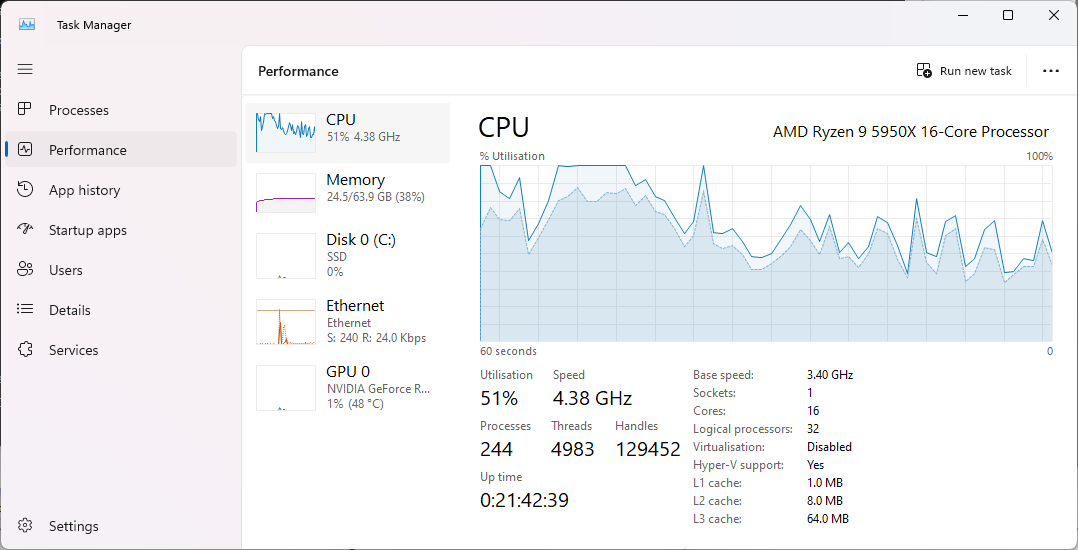
With this PR, most time is spent in user space (light blue):

On higher core count machines, before this PR, the CPU usage becomes
pretty much flat because of contention:
<img width="549" alt="VM_176_windows_heap"
src="https://github.com/llvm/llvm-project/assets/37383324/f27d5800-ee02-496d-a4e7-88177e0727f0">
With this PR, similarily most CPU time is now used:
<img width="549" alt="VM_176_with_rpmalloc"
src="https://github.com/llvm/llvm-project/assets/37383324/7d4785dd-94a7-4f06-9b16-aaa4e2e505c8">
### Changes in this PR
The avenue I've taken here is to vendor/re-licence rpmalloc in-tree, and
use it when building the Windows 64-bit release. Given the permissive
rpmalloc licence, prior discussions with the LLVM foundation and
@lattner suggested this vendoring. Rpmalloc's author (@mjansson) kindly
agreed to ~~donate~~ re-licence the rpmalloc code in LLVM (please do
correct me if I misinterpreted our past communications).
I've chosen rpmalloc because it's small and gives the best value
overall. The source code is only 4 .c files. Rpmalloc is statically
replacing the weak CRT alloc symbols at link time, and has no dynamic
patching like mimalloc. As an alternative, there were several
unsuccessfull attempts made by Russell Gallop to use SCUDO in the past,
please see thread in https://reviews.llvm.org/D86694. If later someone
comes up with a PR of similar performance that uses SCUDO, we could then
delete this vendored rpmalloc folder.
I've added a new cmake flag `LLVM_ENABLE_RPMALLOC` which essentialy sets
`LLVM_INTEGRATED_CRT_ALLOC` to the in-tree rpmalloc source.
### Performance
The most obvious test is profling a ThinLTO linking step with LLD. I've
used a Clang compilation as a testbed, ie.
```
set OPTS=/GS- /D_ITERATOR_DEBUG_LEVEL=0 -Xclang -O3 -fstrict-aliasing -march=native -flto=thin -fwhole-program-vtables -fuse-ld=lld
cmake -G Ninja %ROOT%/llvm -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release -DLLVM_ENABLE_ASSERTIONS=TRUE -DLLVM_ENABLE_PROJECTS="clang" -DLLVM_ENABLE_PDB=ON -DLLVM_OPTIMIZED_TABLEGEN=ON -DCMAKE_C_COMPILER=clang-cl.exe -DCMAKE_CXX_COMPILER=clang-cl.exe -DCMAKE_LINKER=lld-link.exe -DLLVM_ENABLE_LLD=ON -DCMAKE_CXX_FLAGS="%OPTS%" -DCMAKE_C_FLAGS="%OPTS%" -DLLVM_ENABLE_LTO=THIN
```
I've profiled the linking step with no LTO cache, with Powershell, such
as:
```
Measure-Command { lld-link /nologo @CMakeFiles\clang.rsp /out:bin\clang.exe /implib:lib\clang.lib /pdb:bin\clang.pdb /version:0.0 /machine:x64 /STACK:10000000 /DEBUG /OPT:REF /OPT:ICF /INCREMENTAL:NO /subsystem:console /MANIFEST:EMBED,ID=1 }`
```
Timings:
| Machine | Allocator | Time to link |
|--------|--------|--------|
| 16c/32t AMD Ryzen 9 5950X | Windows Heap | 10 min 38 sec |
| | **Rpmalloc** | **4 min 11 sec** |
| 32c/64t AMD Ryzen Threadripper PRO 3975WX | Windows Heap | 23 min 29
sec |
| | **Rpmalloc** | **2 min 11 sec** |
| | **Rpmalloc + /threads:64** | **1 min 50 sec** |
| 176 vCPU (2 socket) Intel Xeon Platinium 8481C (fixed clock 2.7 GHz) |
Windows Heap | 43 min 40 sec |
| | **Rpmalloc** | **1 min 45 sec** |
This also improves the overall performance when building with clang-cl.
I've profiled a regular compilation of clang itself, ie:
```
set OPTS=/GS- /D_ITERATOR_DEBUG_LEVEL=0 /arch:AVX -fuse-ld=lld
cmake -G Ninja %ROOT%/llvm -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release -DLLVM_ENABLE_ASSERTIONS=TRUE -DLLVM_ENABLE_PROJECTS="clang;lld" -DLLVM_ENABLE_PDB=ON -DLLVM_OPTIMIZED_TABLEGEN=ON -DCMAKE_C_COMPILER=clang-cl.exe -DCMAKE_CXX_COMPILER=clang-cl.exe -DCMAKE_LINKER=lld-link.exe -DLLVM_ENABLE_LLD=ON -DCMAKE_CXX_FLAGS="%OPTS%" -DCMAKE_C_FLAGS="%OPTS%"
```
This saves approx. 30 sec when building on the Threadripper PRO 3975WX:
```
(default Windows Heap)
C:\src\git\llvm-project>hyperfine -r 5 -p "make_llvm.bat stage1_test2" "ninja clang -C stage1_test2"
Benchmark 1: ninja clang -C stage1_test2
Time (mean ± σ): 392.716 s ± 3.830 s [User: 17734.025 s, System: 1078.674 s]
Range (min … max): 390.127 s … 399.449 s 5 runs
(rpmalloc)
C:\src\git\llvm-project>hyperfine -r 5 -p "make_llvm.bat stage1_test2" "ninja clang -C stage1_test2"
Benchmark 1: ninja clang -C stage1_test2
Time (mean ± σ): 360.824 s ± 1.162 s [User: 15148.637 s, System: 905.175 s]
Range (min … max): 359.208 s … 362.288 s 5 runs
```
# Conflicts:
# llvm/docs/ReleaseNotes.rst
# llvm/utils/release/build_llvm_release.bat
Copy file name to clipboardExpand all lines: llvm/CMakeLists.txt
+29-1Lines changed: 29 additions & 1 deletion
Original file line number
Diff line number
Diff line change
@@ -718,7 +718,35 @@ if( WIN32 AND NOT CYGWIN )
718
718
endif()
719
719
set(LLVM_NATIVE_TOOL_DIR""CACHEPATH"Path to a directory containing prebuilt matching native tools (such as llvm-tblgen)")
720
720
721
-
set(LLVM_INTEGRATED_CRT_ALLOC""CACHEPATH"Replace the Windows CRT allocator with any of {rpmalloc|mimalloc|snmalloc}. Only works with CMAKE_MSVC_RUNTIME_LIBRARY=MultiThreaded.")
721
+
set(LLVM_ENABLE_RPMALLOC""CACHEBOOL"Replace the CRT allocator with rpmalloc.")
722
+
if(LLVM_ENABLE_RPMALLOC)
723
+
if(NOT (CMAKE_SYSTEM_NAMEMATCHES"Windows|Linux"))
724
+
message(FATAL_ERROR"LLVM_ENABLE_RPMALLOC is only supported on Windows and Linux.")
725
+
endif()
726
+
if(LLVM_USE_SANITIZER)
727
+
message(FATAL_ERROR"LLVM_ENABLE_RPMALLOC cannot be used along with LLVM_USE_SANITIZER!")
set(LLVM_INTEGRATED_CRT_ALLOC"${LLVM_INTEGRATED_CRT_ALLOC}"CACHEPATH"Replace the Windows CRT allocator with any of {rpmalloc|mimalloc|snmalloc}. Only works with CMAKE_MSVC_RUNTIME_LIBRARY=MultiThreaded.")
722
750
if(LLVM_INTEGRATED_CRT_ALLOC)
723
751
if(NOTWIN32)
724
752
message(FATAL_ERROR"LLVM_INTEGRATED_CRT_ALLOC is only supported on Windows.")
0 commit comments