-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 1.3k
Description
ISSUE TYPE
- Enhancement Request
COMPONENT NAME
StatsCollector
CLOUDSTACK VERSION
4.17
SUMMARY
This spec changes the way Apache CloudStack collects and stores the VM stats to make the data more consistent and provide historical data.
Table of Contents
- Problem description
1.1. Current collecting/storing data workflows and possible configurations
1.2. Current data cleaning workflow
1.3. Current API - Proposed changes
2.1. Proposed collecting/storing data workflow
2.2. Configuration proposal
2.3. Data cleaning proposal
2.4. New API proposal
2.5. UI adjustment proposal - Work items
3.1. Database tables
3.2. Global configurations
3.3. API
3.4. UI - Future works
1. Problem description
In Apache CloudStack (ACS), VM stats are collected by Management Servers. Currently, each Management Server collects the data independently and stores it only in (primary) memory. This model of collecting and storing VM stats results in some limitations, numbered as follows:
-
When restarting a Management Server (or when it crashes), the VMs stats data is lost (since there is no data persistence);
-
When the cloud is composed of multiple Management Servers, each one of them can show different data about the VMs, as there is no centralization or synchronization of the data collected by different Management Servers;
-
It is not possible to obtain historical data. The reasons for this are: i) ACS stores either the accumulative/aggregated of collected data or only the most recently collected data point (see Section 1.1 for details); ii) even if you were to consider storing multiple collected data points and presenting a history for each individual Management Server (due to limitation 2), there would be no guarantee that data from a certain period would exist (see limitation 1).
The next subsections describe in more details how the collection of VM stats is currently designed and implemented by ACS. Only the most relevant points for this spec are presented.
1.1. Current collecting/storing data workflows and possible configurations
Currently, each Management Server perform its own VM stats collection. This data is collected only from VMs that are running. The collected data is only stored in a concurrent hash map in memory, where keys are VM IDs and values are stats. Since there is no data being shared or synced between Management Servers, the stats about a VM can be different in each one of them.
It is possible to configure the interval between data gathering with the global configuration vm.stats.interval, which is defined in milliseconds.
The global configuration vm.stats.increment.metrics.in.memory (which is set by a boolean value) allows operators to define whether i) data should be stored incrementally (i.e., accumulating the data); or ii) in such a way as to keep only the data from the most recent collection (i.e., a data replacement).
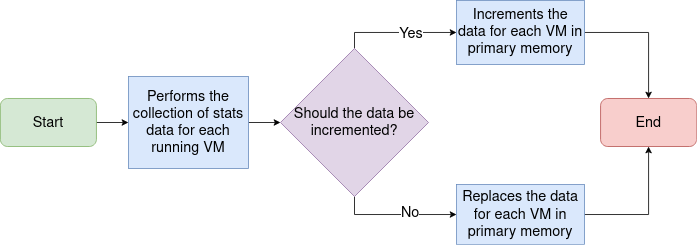
Figure 1 illustrates the current collecting and storing data workflows.
Figure 1: The current workflow to collect and store VM stats performed periodically for each Management Server.
1.2. Current data cleaning workflow
In the latest ACS release (4.16.0), no cleanup of VM stats data is performed, which leads Management Servers to continue to show them even for VMs that are no longer running (e.g., VMs that have changed to states such as 'stopping', 'stopped', 'destroyed', 'expunging', and so on). PR #5633, already approved and merged, addresses the issue of data cleaning considering the current collecting and storing VM stats workflow (i.e., the cleanup is done with no concern for providing historical data).
1.3. Current API
The current implemented API, listVirtualMachinesMetrics, just extends the listVirtualMachines API, so it inherits all of its parameters, even if some of them are not suitable/useful for the API purpose. Also, although the official documentation states that only tags related to metrics are returned, the current API returns all the same information as the listVirtualMachines API. Finally, if the listVirtualMachinesMetrics API is called passing in the details parameter a comma-separated list that does not include the stats attribute, it does not return the VM stats as, again, it has the same behavior as the listVirtualMachines API.
2. Proposed changes
This spec proposes to change the way ACS collects and stores the VM stats. The intent is to make the data presented by Management Servers more consistent and also provide historical data. The proposal changes are described in the next subsections.
2.1. Proposed collecting/storing data workflow
For storing, our proposal is to persist the VM stats in the database (MySQL); however, we see the opportunity for the future to have options to choose between different metrics storage backends such as InfluxDB, Mongo, and so on. In addition, the data will be stored in a collected data point format. In this context, a collected data point represents a single collection of all stats for a specific VM, performed by a given Management Server. Each collected data point will have a timestamp that indicates when the collection was performed. The data collection will continue to work the same way: at each collection round, each Management Server collects the stats from all running VMs.
This new approach will allow ACS users to obtain historical data. Also, it will logically centralize the data. Thus, all Management Servers will show the same data about each VM.
Figure 2 illustrates the proposal for the new data collection and storage workflow.
Figure 2: The proposed workflow to collect and store VM stats performed periodically for each Management Server.
2.2. Configuration proposal
Since the data will now be persisted in the database instead of being kept only in primary memory, we propose to change the global configuration vm.stats.increment.metrics.in.memory to just vm.stats.increment.metrics. We also propose that this configuration will no longer control how data is stored; since data will always be stored in collected data points format (never incrementally). Instead, this configuration will now indicate how data is returned by the API by default (see subsections 2.4 and 3.3 for details).
We also propose to create a new global configuration called vm.stats.max.retention.time. It defines how long the collected data points should be stored so that the oldest records can be automatically deleted as theirs time to live (TTL) is reached.
Finally, we propose that the VM stats collection process be disabled by setting the global configuration vm.stats.interval to 0 or less than 0.
2.3. Data cleaning proposal
We propose two types of data cleanup process. The first one automatically removes old records, which are collected data points that have a timestamp indicating that the time limit set in the global configuration vm.stats.max.retention.time has been exceeded. If vm.stats.max.retention.time be set to 0 or less than 0, then this automatic removal process will be disabled. The second cleanup process removes all collected data points related to VMs that were destroyed. Therefore, the cleaning mechanisms added by PR #5633 in order to remove stats for VMs that are no longer running will be removed.
2.4. New API proposal
For compatibility reasons, we propose to keep the current API and create a new one to handle historical reporting of VM stats. The current API, listVirtualMachinesMetrics, will have only minimal changes to work with the new data storage mode (see subsection 3.3 for details). The new API, called listVirtualMachinesUsageHistory, allows ACS users to get historical data filtered by specific time periods. For this, the API has the parameters startdate and enddate, which allow ACS users to do 4 different types of filtering:
-
Get all VM stats starting at a given time (by passing only the startdate parameter);
-
Get all VM stats up to a given time (by passing only the
enddateparameter); -
Get all VM stats from a specific time range (by passing both the
startdateandenddateparameters, so thatstartdateis beforeenddate); -
Get all VM stats with a specific timestamp (by passing both the
startdateandenddateparameters, so thatstartdateequals
enddate).
In addition, it is possible to combine these parameters with other parameters offered by the API (see all parameters in Table 1). This API returns just the stats data and essential information to identify the VMs. All response tags are described in Table 2.
| Parameter Name | Description |
|---|---|
| id | The ID of the virtual machine. |
| ids | The IDs of the virtual machines, mutually exclusive with id. |
| keyword | List by keyword. |
| page | The page number. |
| pagesize | The page size. |
| name | Name of the virtual machine (a substring match is made against the parameter value, data for all matching VMs will be returned). |
| startdate | Start date to filter VM stats. |
| enddate | End date to filter VM stats. |
Table 1: ThelistVirtualMachinesUsageHistory request parameters.
| Response Name | Description |
|---|---|
| id | The ID of the virtual machine. |
| name | The name of the virtual machine. |
| stats (*) | The virtual machine stats. |
| timestamp | The time when the stats were collected. |
| cpuused | The amount (percentage) of the VM's CPU currently used. |
| diskioread | The read (I/O) of disk on the VM. |
| diskiowrite | The write (I/O) of disk on the VM. |
| diskread | The disk read in MiB. |
| diskwrite | The disk write in MiB. |
| diskkbsread | The read (bytes) of disk on the VM. |
| diskkbswrite | The write (bytes) of disk on the VM. |
| memoryintfreekbs | The internal memory that's free in VM or zero if it can not be calculated. |
| memorykbs | The memory used by the VM in Kbps. |
| memorytargetkbs | The target memory in VM in Kbps. |
| networkread | The network read in MiB. |
| networkwrite | The network write in MiB. |
| networkkbsread | The incoming network traffic on the VM. |
| networkkbswrite | The outgoing network traffic on the host. |
Table 2: The listVirtualMachinesUsageHistory response tags.
2.5. UI adjustment proposal
The UI continues to consume the same API (listVirtualMachinesMetrics) to show VM stats. The only change is that it now only shows stats data for VMs with the running state.
3. Work items
This section describes all work items to implement the proposal.
3.1. Database tables
No existing tables are modified, there is only one new table to be created: table vm_stats, where each record represents a collected data point.
| Column | Nullable | Updatable | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| id | No | No | To identify the collected data point. |
| vm_id | No | No | To identify the related VM. |
| mgmt_server_id | No | No | Indicates which Management Server collected the data. |
| timestamp | No | No | Indicates the instant the collected data point was created (i.e., when the data was collected). |
| vm_stats_data | No | No | The collected data in JSON format. These are the same data that is currently stored only in memory. |
Table 3: Database table vm_stats.
3.2. Global configurations
-
Rename the global configuration
vm.stats.increment.metrics.in.memorytovm.stats.increment.metrics; -
Create the global configuration
vm.stats.max.retention.time; -
Change
StatsCollectorto disable the automatic removal process of VM stats records when the global configurationvm.stats.max.retention.timeis set to 0 or less than 0; -
Change
StatsCollectorto disable the VM stats collection when the global configuration vm.stats.interval` is set to 0 or less than 0.
3.3. API
-
Adjust the listVirtualMachinesMetrics API to get data from the database instead of the in-memory map;
-
Add a new parameter called
accumulate(set by a boolean value) to API listVirtualMachinesMetrics that allows ACS users force the API to return data in either accumulative or non-accumulative mode. This overwrites the global configurationvm.stats.increment.metrics. Whenaccumulateparameter is not passed, stats are returned according to the global configurationvm.stats.increment.metrics; -
Create the new API listVirtualMachinesUsageHistory with all request parameters described in Table 1 and all response tags described in Table 2;
-
Annotate the listVirtualMachinesMetrics API as deprecated so that in the future it can be replaced by the new API.
3.4. UI
-
Adjust the UI to show only the most recent stats for each VM;
-
Adjust the UI to not show stats for VMs that are no longer running, even though the API returns the historical stats data for those VMs.
4. Future works
-
Implement new views, in UI, to show history of VM stats;
-
Evaluate if there are other useful parameters to add to the listVirtualMachinesUsageHistory API.